
Increases Heart Rate
- Nicotine causes the release of adrenalin and noradrenalin, which are hormones produced by the adrenal glands.
- Once nicotine is absorbed by the alveoli in the lungs or the mucous membranes of the nose, it stimulates the release of adrenalin and noradrenalin, which are collectively referred to as catecholamines.
How does nicotine affect the nervous system?
What is the role of nicotine in the nervous system?
What are the main contributors to atherogenesis and thrombogenesis from cigarette smoke?
How long does nicotine last in the body?
What are the toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke?
What is cigarette smoke?
How many chemicals are in cigarettes?
See 4 more
About this website
Cardiovascular toxicity of nicotine: implications for nicotine ...
This review discusses the known cardiovascular effects of smoking and the effects of nicotine without tobacco smoke and interprets the available data on cardiovascular risk during nicotine replacement therapy (NRT). Nicotine gum and patches are now approved for over the counter sale in the United St …
Is It the Nicotine Itself That Constricts Blood Vessels?
Hello, The answer is "YES"! Nicotine is a vasoconstrictor, meaning it will narrow the arteries supplying oxygen to the tissues. This can lead to complications in wound healing especially in surgeries requiring elevation of flaps, such as facelifts, breast reductions and tummy tucks.
The Effects of Nicotine on the Cardiovascular System
Nicotine causes the release of adrenalin and noradrenalin, which are hormones produced by the adrenal glands. Once nicotine is absorbed by the alveoli in the lungs or the mucous membranes of the nose, it stimulates the release of adrenalin and noradrenalin, which are collectively referred to as catecholamines.
Nicotine effect on cardiovascular system and ion channels
Smoking is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Nicotine is one of the components of cigarette smoke. Nicotine effects on the cardiovascular system reflect the activity of the nicotine receptors centrally and on peripheral autonomic ganglia. It …
Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease - Centers for Disease Control and ...
Title: Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease Author: HHS/CDC Subject: Fact Sheet Keywords: smoking, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease ...
Why is vaping bad after a workout?
During a workout this is bad and unwanted because it is going to cause you to burn through your energy quicker than normal. This same issue applies to you after a workout also. If you are vaping after your workout, you are preventing your body from properly cooling down.
How Can I Improve my Lungs After Vaping?
While knowing you may have cardio issues from vaping many look to lessening their vaping around their workouts instead of quitting it overall. As to this they wondering how to improve their lungs after vaping.
Can Vaping Affect Your Stamina?
Since it can impact your lungs and your cardiovascular system it is very possible that it will impact your stamina, especially on heavily cardiac based activities.
Does Vaping Affect Lung Capacity?
Vaping is shown to increase lung inflammation which can lead to issues with overall capacity to hold oxygen and use oxygen,
Does Nicotine Affect Cardio?
Nicotine is a highly addictive chemical which makes is dangerous but its secondary effects are tied to cardiovascular issues with increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Does Vaping Make You Gain Weight?
While the effects of vaping do appear to be overall negative the one large benefit that it shares with tobacco smoking is that it can help with weight loss.
Does Vaping Affect Muscle Growth?
Most people assume that vaping is a better choice alternative to smoking and perfectly fine before or after a workout. The problem with this thinking is that while the vapor in e-cigs is much more kind on your lungs, it does nothing about the nicotine contained.
What does nicotine do to your body?
That means that when the e-juice is vaped, the nicotine gives one’s nervous system a kick-start to increase the body’s energy level. It also increases the heart rate a bit.
Why is vaping important?
Using a vape pen that contains nicotine can help in controlling one’s weight. This is important for the maintenance of correct posture among athletes.
Can you vape without smoking?
If you are starting to vape without smoking in the past, the impact may be the opposite. You have to bear in mind that any chemical that is carried to the lungs constitutes a level of risk to the lungs and one’s general health. One of the benefits of the switch from smoking to vaping is the decrease of systolic blood pressure, which is the measure of the pressure placed on the arteries during heart contractions. Smoking has been known to increase pressure. When you switch from smoking to vaping, you will see an improvement in your blood pressure. However, when you vape for the first time and without any smoking experience, you are likely to notice a reduction in cardio performance although these may be less substantially compared to smoking cigarettes.
Is vaping good for you?
In general vaping and running have adverse effects on your performance. However, if you are a smoker, vaping taken as an alternative to cigarette smoking can be more beneficial to health. It also helps you to perform your exercise routines better due to the lack of cigarette smoke . It is also a sustainable method of eliminating nicotine and tobacco product for good.
Is vaping better than smoking?
Some health experts claim that vaping is 95 percent safer for health than smoking. Some studies also showed some positive impacts of vaping on athletic performance. Some of the positive effects of vaping on physical performance include better cardio performance, stronger stamina, having increased energy, a much better mood, and weight control.
Is it safe to vape?
This may not be the same though when you vape or smoke for the first time.
Is smoking bad for athletic performance?
Smoking has been established as a no-no when it comes to athletic performance. Its harmful effects are already proven by research. According to research, nicotine speeds up the heart rate and narrows one’s arteries. Smoking can increase blood pressure. It is also known for having harmful effects that can reduce the physical performance of an athlete.
Why are teens addicted to vaping?
Due to the convenience of e-cigarettes along with their seemingly harmless nature and tasty flavors, teens and young adults who had never previously smoked cigarettes or used tobacco products are becoming addicted to vaping at an alarming rate.
How many people use vaping?
Since being introduced in 2007, vaping trends are estimated to have increased by nearly 14-fold in just the last decade. Now used by an estimated 1 in 20 Americans, e-cigarettes have become a rising public health concern mainly due to their alarming popularity among teens and young adults. In 2018, the FDA estimated that 3.6 million middle and high school students consider themselves e-cigarette users. Due to the convenience of e-cigarettes along with their seemingly harmless nature and tasty flavors, teens and young adults who had never previously smoked cigarettes or used tobacco products are becoming addicted to vaping at an alarming rate. Despite growing health precautions associated with vaping, the market continues to grow. There are currently 460 brands of e-cigarettes and over 7,700 flavors.
What is an e-cigarette?
Invented as a safer alternative to smoking cigarettes, e-cigarettes are battery-operated, handheld devices that are meant to replace the act of smoking a cigarette.
How many brands of e-cigarettes are there?
There are currently 460 brands of e-cigarettes and over 7,700 flavors. Even though e-cigarettes lack the harmful carcinogens that are present in normal cigarettes, the chemicals and nicotine levels in the e-liquids may pose an even deadlier threat.
Is vaping a good alternative to smoking cigarettes?
For adults who are trying to quit smoking, vaping can be a safer alternative to smoking conventional cigarettes. Even though these electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) could decrease the risk of cancer in regular smokers, other health hazards associated with vaping have been unclear until now.
Can smoking cigarettes cause stroke?
A further analysis of this data also showed that regardless of how frequently someone uses e-cigarettes, they are still more likely to suffer a heart attack or develop coronary artery disease. Smoking cigarettes and vape pens both cause high blood pressure as well, which is the leading cause of stroke. For adults monitoring high blood pressure , one of the first recommendations doctors give is to stop smoking. Young people can have high blood pressure too and sometimes don’t even know they have it until later in life.
Does smoking e-cigarettes cause heart problems?
With a risk of heart failure higher than 50 percent, e-cigarette smoking clearly carries some heavy heart risks. The e-liquids that are present in e-cigarettes also contain chemicals that are toxic to the endothelial cells that line the interior of blood vessels and play an important role in heart health. A recent study found that when exposed to the e-liquids in vape pens, the endothelial cells died and were unable to form new vascular tubes. The severity of the damage seemed to vary depending on the flavor of the e-liquid.
How does nicotine affect the nervous system?
The systemic hemodynamic effects of nicotine are mediated primarily by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Nicotine releases norepinephrine from adrenergic neurons and increases adrenal release of epinephrine (3). Sympathetic stimulation is thought to be a result of activation of nAChRs in the peripheral nervous system, such as the carotid chemoreceptor, as well as by central nervous system nAChR activation.
What is the role of nicotine in the nervous system?
Nicotine acts on pentameric nAChRs throughout the nervous system (brain, autonomic nervous system, and skeletal-muscle), as well as some non-neuronal sites (2, 3). The subunit composition of nAChRs varies by tissue and conveys different agonist binding and electrophysiologic characteristics. Nicotine binds to the outside of the channel and activates the release of various neurotransmitters, including catecholamines. The α4 β2 receptor is thought to mediate nicotine addiction. α3 β4 receptors, present in autonomic ganglia and the adrenal gland, mediate cardiovascular responses. α7 homomeric receptors, are present not only in the brain but also in non-neuronal tissue such as endothelial cells, airway epithelial cells, inflammatory cells (lymphocytes and macrophages) and keratinocytes.
What are the main contributors to atherogenesis and thrombogenesis from cigarette smoke?
Oxidizing chemicals such as free radicals (a puff of cigarette contains 1017), reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species are thought to be the main contributors to atherogenesis and thrombogenesis from cigarette smoke. Oxidative damage occurs by endothelial cell activation, dysfunction and damage (both reducing bioavailability of nitric oxide [NO] and depleting endogenous antioxidants), inflammation, platelet activation, and lipid abnormalities (3, 7).
How long does nicotine last in the body?
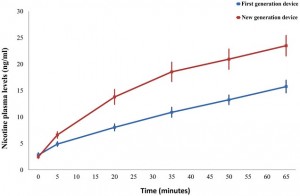
Nicotine has an average terminal half-life of two hours. With regular dosing blood nicotine levels rise over 6-8 hours, then plateau throughout the rest of the day during smoking. The pattern of human exposure is a combination of intermittent peaks and troughs throughout the day, with gradually declining nicotine exposure overnight. Typically average blood nicotine concentrations are 10-40ng/ml. Levels in the brain or heart are 2-3 fold higher.
What are the toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke?
Toxic organic chemicals in cigarette smoke include polycyclic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and reactive aldehydes such as acrolein, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. PAHs accelerate atherosclerosis in some animal models. Aldehydes form reactive oxygen species with downstream effects described above (3, 6, 7). Additionally, acrolein co-localizes with intimal atherosclerotic macrophages, modifies apolipoprotien A-1, the major protein in HDL, contributes to endothelial damage, enhances thrombogenesis (by activating platelets and inhibiting antithrombin), and causes coronary vasospasm in animal studies.
What is cigarette smoke?
Cigarette smoke consists of an aerosol of particulates carried in a gas phase. Smoke particulates are droplets containing solid carbonaceous materials, with characteristic diameter-dependent airway deposition patterns (9). In diameters <2.5 μm they are known as “fine” and “ultra-fine” (PM2.5and PM0.1respectively), deposit in alveoli, and can even pass into the pulmonary and systemic circulations. Inhalation of particulates results in oxidative injury, vascular inflammation, platelet activation, increased blood viscosity, and altered cardiac autonomic function. Chronic particulate inhalation, from cigarette smoke as well as from environmental pollution, results in non-linear dose-response increases in cardiovascular risk, and is considered a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
How many chemicals are in cigarettes?
Cigarette smoke contains more than 9,000 chemicals, and greater than 69 known carcinogens, the vast majority of which are products of tobacco combustion (3, 6). Constituents of most concern with respect to cardiovascular disease are: 1) oxidizing chemicals, 2) carbon monoxide, 3) volatile organic compounds 4) particulates, 5) heavy metals and 6) nicotine.
Does vaping affect fitness?
At this point, vaping is still a bit of an un known in several respects, so unfortunately it's not definitively known how vaping can impact your fitness. This is particularly true of long-term effects, as it simply hasn't been around long enough to do that kind of study. So, what we're left with is anecdotal evidence. While these kinds of accounts should be taken with a pinch of salt, they shouldn't be ignored either if lots of people are saying the same thing; that their cardio has improved after giving up smoking for vaping.
Is This Down to Quitting Smoking?
While not all vapers quit smoking altogether, many significantly reduce the number of cigarettes they're smoking.
How does electronic cigarettes affect the cardiovascular system?
Impact of Electronic Cigarettes on the Cardiovascular System. Tobacco smoking is a major public health threat for both smokers and nonsmokers. There is accumulating evidence demonstrating that smoking causes several human diseases, including those affecting the cardiovascular system.
What are the health effects of smoking e-cigarettes?
Recent clinical and animal studies showed that (active or passive) e‐vapors/e‐cigarettes may cause irritation of both the upper and lower respiratory tract, in addition to inducing bronchospasm and cough 9, 32, 33, 34; the latter effects may be attributed to a chain of inflammatory reactions through oxidative stress. 28
Why are e-cigarettes dangerous?
Additional concerns related to e‐cigarettes include nicotine dependence and toxicity, given that the nicotine concentrations found in plasma of e‐cigarette smokers are high enough to produce and maintain nicotine dependence, especially in youth. This may explain why many adolescents shift to tobacco smoking in their adulthood or cannot abandon vaping easily. 22 E‐cigarettes may also present higher risks of nicotine toxicity, especially for children, because some incidents of ingesting e‐liquids were reported. 9, 119 In fact, the number of calls to poison centers for ingestion of e‐liquids increased from “one per month in September 2010 to 215 per month in February 2014”. 120 Thus, the Child Nicotine Poisoning Prevention Act was initiated in January 2016; this required e‐cigarettes manufacturers to use child‐resistant e‐liquid packaging.
What is an e-cigarette?
E‐cigarettes, also known as vape pens, e‐cigars, or vaping devices, are electronic nicotine delivering systems, which generate an aerosolized mixture containing flavored liquids and nicotine that is inhaled by the user. 9 The extensive diversity of e‐cigarettes arises from the various nicotine concentrations present in e‐liquids, miscellaneous volumes of e‐liquids per product, different carrier compounds, additives, flavors, and battery voltage. 9 Regardless of the exact design, each e‐cigarette device has a common functioning system, which is composed of a rechargeable lithium battery, vaporization chamber, and a cartridge (Figure 1 ). The lithium battery functions as the powerhouse; it is connected to the vaporization chamber that contains the atomizer 9 (Figure 1 ). In order to deliver nicotine to the lungs, the user inhales through a mouthpiece, and the airflow triggers a sensor that then switches on the atomizer. 9, 10, 11 Finally, the atomizer vaporizes liquid nicotine in a small cartridge (Figure 1) and delivers it to the lungs. 9
How successful are e-cigarettes?
Since their introduction in 2007, e‐cigarettes have experienced widespread success among smokers, nonsmokers, pregnant females, and even youth. Their sales increased by 14‐fold since 2008, 15 contributing to scientists' desire/necessity to evaluate their safety, population patterns, and usage reasons. 16 Usage patterns vary depending on consumers' age group. 4 In adults, usage increased over the past decade to include 3.8% of US adults, of which almost 16% are current cigarette smokers, whereas 22% are former smokers. 17 Importantly, almost 3.2% of individuals who never smoked before/naïve have tried e‐cigarettes, reflecting exposure to harmful chemicals for “neoteric” purposes. 17, 18 In fact, adults primarily use e‐cigarettes to discontinue smoking because they perceive them to be: (1) a healthier choice, which can reduce nicotine cravings, and (2) less harmful to nonusers in their proximity. 4, 19 As for seniors, it appears that e‐cigarettes are used to stop smoking or to bypass smoke‐free policies. 20, 21
How is nicotine metabolized?
93 After absorption, nicotine is metabolized by the liver into cotinine as one of the metabolites. 94 Most e‐liquids contain nicotine at concentrations that vary between 0 and 36.6 mg/mL. 95 Interestingly, it has been reported that several e‐cigarette brands inaccurately labeled nicotine concentration, 96 and, in fact, some of the “nicotine free” brands apparently contain some. 8 As expected, e‐liquids with higher nicotine concentrations deliver more nicotine than those with lower concentrations. 43, 97
Why do teens use e-cigarettes?
Usage of e‐cigarettes among the youth is mainly linked to their curiosity and the “appealing” flavored nature of e‐liquids. 19 It is alarming that this group has the highest increase in usage 18; 5.3% of all users are middle school students, and 16% are high school students. This is a 9‐ and 10‐fold increase, respectively, since 2011. 18 Because the brain is only fully developed by the age of mid‐twenties, youths' exposure to nicotine may disrupt their brain development, and hinder attention and learning, while elevating susceptibility for addiction to nicotine or other drugs such as cocaine. 22
Why Do People Vape?
First of all, let’s look at why vaping has become so popular and why people vape.
How many people stopped vaping in 2015?
However, the number of people using vaping to stop smoking started to decline in 2015, with only 30% of people using vaping to stop smoking. During this time, the importance of social image started to increase (37% of people), and more people began vaping because of this.
Is vaping good for runners?
Alternatively, if you are a regular smoker, replacing smoking with vaping can be a healthier option. It may also help you perform better through the lack of cigarette smoke.
Does vaping harm your lungs?
However, several studies have indicated that vaping can harm the lungs and these results included both with and without nicotine. So as the studies show, combining vaping and running is detrimental to your performance. If your a serious runner looking to improve your times, stay away from both nicotine and vaping.
Does vaping affect performance?
Although the study did somewhat prove vaping affects performance, it also stated that more research is needed to provide adequate evidence to support this. Many vapers have though reported increased performance in running, cycling, and swimming. However, we cannot prove this is a result of vaping alone.
Can vaping improve performance?
Although often debated, some studies have shown that after vaping, athletes were able to perform better. This improvement only happened when vaping occurred a few hours before exercise.
Can you run with e-cigarettes?
While this may all seem relatively positive, if you runner doing large volume each week , you must be careful of your respiratory systems. This study showed that e-cigarette user’s respiratory systems are often affected and more susceptible to increased respiratory infections and delayed recovery.
How does nicotine affect the nervous system?
The systemic hemodynamic effects of nicotine are mediated primarily by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Nicotine releases norepinephrine from adrenergic neurons and increases adrenal release of epinephrine (3). Sympathetic stimulation is thought to be a result of activation of nAChRs in the peripheral nervous system, such as the carotid chemoreceptor, as well as by central nervous system nAChR activation.
What is the role of nicotine in the nervous system?
Nicotine acts on pentameric nAChRs throughout the nervous system (brain, autonomic nervous system, and skeletal-muscle), as well as some non-neuronal sites (2, 3). The subunit composition of nAChRs varies by tissue and conveys different agonist binding and electrophysiologic characteristics. Nicotine binds to the outside of the channel and activates the release of various neurotransmitters, including catecholamines. The α4 β2 receptor is thought to mediate nicotine addiction. α3 β4 receptors, present in autonomic ganglia and the adrenal gland, mediate cardiovascular responses. α7 homomeric receptors, are present not only in the brain but also in non-neuronal tissue such as endothelial cells, airway epithelial cells, inflammatory cells (lymphocytes and macrophages) and keratinocytes.
What are the main contributors to atherogenesis and thrombogenesis from cigarette smoke?
Oxidizing chemicals such as free radicals (a puff of cigarette contains 1017), reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species are thought to be the main contributors to atherogenesis and thrombogenesis from cigarette smoke. Oxidative damage occurs by endothelial cell activation, dysfunction and damage (both reducing bioavailability of nitric oxide [NO] and depleting endogenous antioxidants), inflammation, platelet activation, and lipid abnormalities (3, 7).
How long does nicotine last in the body?
Nicotine has an average terminal half-life of two hours. With regular dosing blood nicotine levels rise over 6-8 hours, then plateau throughout the rest of the day during smoking. The pattern of human exposure is a combination of intermittent peaks and troughs throughout the day, with gradually declining nicotine exposure overnight. Typically average blood nicotine concentrations are 10-40ng/ml. Levels in the brain or heart are 2-3 fold higher.
What are the toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke?
Toxic organic chemicals in cigarette smoke include polycyclic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and reactive aldehydes such as acrolein, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. PAHs accelerate atherosclerosis in some animal models. Aldehydes form reactive oxygen species with downstream effects described above (3, 6, 7). Additionally, acrolein co-localizes with intimal atherosclerotic macrophages, modifies apolipoprotien A-1, the major protein in HDL, contributes to endothelial damage, enhances thrombogenesis (by activating platelets and inhibiting antithrombin), and causes coronary vasospasm in animal studies.
What is cigarette smoke?
Cigarette smoke consists of an aerosol of particulates carried in a gas phase. Smoke particulates are droplets containing solid carbonaceous materials, with characteristic diameter-dependent airway deposition patterns (9). In diameters <2.5 μm they are known as “fine” and “ultra-fine” (PM2.5and PM0.1respectively), deposit in alveoli, and can even pass into the pulmonary and systemic circulations. Inhalation of particulates results in oxidative injury, vascular inflammation, platelet activation, increased blood viscosity, and altered cardiac autonomic function. Chronic particulate inhalation, from cigarette smoke as well as from environmental pollution, results in non-linear dose-response increases in cardiovascular risk, and is considered a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
How many chemicals are in cigarettes?
Cigarette smoke contains more than 9,000 chemicals, and greater than 69 known carcinogens, the vast majority of which are products of tobacco combustion (3, 6). Constituents of most concern with respect to cardiovascular disease are: 1) oxidizing chemicals, 2) carbon monoxide, 3) volatile organic compounds 4) particulates, 5) heavy metals and 6) nicotine.
