
Causes
While pulmonary granulomatous disease has been well-studied in cases of chronic silica and asbestos exposure, it appears that vaping-related granulomatous disease may be a separate, reversible entity. 11,12 Similar reports would justify studying the association between vaping initiation and development of pulmonary granulomatous disease.
Symptoms
Summary Summary. Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare, inherited immunodeficiency that affects certain white blood cells. People with this condition have immune systems that do not function properly, leaving the body vulnerable to chronic inflammation and frequent bacterial and fungal infections.
Complications
Vaping E-cigarettes linked to lung problems, first long-term study on vaping finds Vaping can harm your lungs relatively quickly, increasing the risk of conditions like asthma and bronchitis. New research explores the long-term health effects of using e-cigarettes.
Does vaping increase the risk of pulmonary granulomatous disease?
Some veterans may have complications with CGD as the result of their military service. If you are a veteran who developed chronic granulomatous disease as the result of your military service, you may be entitled to compensation through VA disability benefits. What is Chronic Granulomatous Disease?
What is chronic granulomatous disease?
What are the long term effects of vaping?
Does chronic granulomatous disease qualify for VA disability benefits?
What was the diagnosis of a 34 year old woman who had a dry cough and dyspnea?
Is vaping a pulmonary disease?
Is vaping a pulmonary granulomatous disease?
About this website
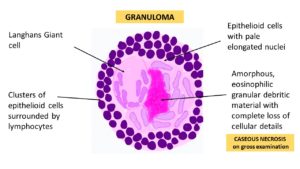
What diseases could you get from vaping?
These aldehydes can cause lung disease, as well as cardiovascular (heart) disease. E-cigarettes also contain acrolein, a herbicide primarily used to kill weeds. It can cause acute lung injury and COPD and may cause asthma and lung cancer.
Can vaping cause chronic lung disease?
June 17, 2022 – A study that looked at four patients with chronic lung disease found that e-cigarette use was the most likely cause.
Can vaping cause chronic inflammation?
Chemicals used for vaping break down zipper-like junctions between cells in the gut, leading to chronic inflammation and potential for other health concerns.
Can smoking cause granulomas?
Tobacco smoke exposure of mice produces interstitial granulomatous inflammation similar to Langerhans cell granulomatosis in humans. The elevated level of pulmonary Langerhans cells implicate these cells in the pathogenesis of these lesions.
How long does it take for vaping to cause permanent damage?
Exposure for just three days was enough to incur sufficient damage to their lungs, setting the stage for long-term chronic lung damage.
What are the symptoms of lung damage from vaping?
What are the symptoms of EVALI?Shortness of breath.Cough.Chest pain.Fever and chills.Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.Rapid heartbeat.Rapid and shallow breathing.
Can vaping cause granulomas in the lungs?
This case report describes reversible pulmonary granulomatous disease and reaffirms an association between vaping and lung injury, evidenced clinically and radiographically. Moreover, it characterizes a chronological history of granuloma development after vaping initiation, followed by resolution upon cessation.
What organs are affected by vaping?
Organs (brain, heart, kidneys, lungs, liver): Heavy metals in vapor can build up in the blood and organs and cause damage.
Is vaping worse than smoking?
1: Vaping is less harmful than smoking, but it's still not safe. E-cigarettes heat nicotine (extracted from tobacco), flavorings and other chemicals to create an aerosol that you inhale. Regular tobacco cigarettes contain 7,000 chemicals, many of which are toxic.
What causes granulomatous inflammation?
Causes. CGD is caused by defects in an enzyme, NADPH oxidase, that phagocytes need to kill certain bacteria and fungi. Mutations in one of five different genes can cause these defects.
Are calcified granulomas permanent?
Over time, granulomas can become calcified or bone-like, and cause permanent damage. Because it can affect any organ, or multiple organs at the same time, sarcoidosis takes on different forms.
What causes granulomas to form?
Granulomas form when immune cells clump together and create tiny nodules at the site of the infection or inflammation. A granuloma is the body's way: to contain an area of bacterial, viral or fungal infection so it can try to keep it from spreading; or. to isolate irritants or foreign objects.
What are the long term side effects of vaping?
These risks include nicotine addiction, mood disorders, and permanent lowering of impulse control. Nicotine also changes the way synapses are formed, which can harm the parts of the brain that control attention and learning.
How do lungs heal from vaping?
However, there are certain lifestyle behaviors you can practice to try and accelerate the rate at which your lungs heal.Drink Lots Of Water. ... Eat Healthy Foods. ... Exercise Regularly. ... Cough. ... Clean Your Living Space. ... Practice Deep Breathing. ... Try Steam Therapy.
Can a doctor tell if you vape?
Medical tests can detect nicotine in people's urine, blood, saliva, hair, and nails. Nicotine is the addictive substance in tobacco, cigarettes, and vapes or e-cigarettes.
Is vaping worse than smoking cigarettes?
1: Vaping is less harmful than smoking, but it's still not safe. E-cigarettes heat nicotine (extracted from tobacco), flavorings and other chemicals to create an aerosol that you inhale. Regular tobacco cigarettes contain 7,000 chemicals, many of which are toxic.
What was the diagnosis of a 34 year old woman who had a dry cough and dyspnea?
A 34 year old woman presented to clinic with dry cough and dyspnea. She was a former cigarette smoker (four pack-years, quit at age 32). Her medical history was significant for a low-grade carcinoid tumor, which was discovered the year prior when she had sought evaluation for recurrent pneumonia and wheezing. At that time, due to airway obstruction, she had undergone right middle and lower lobectomies, and her symptoms resolved shortly thereafter.
Is vaping a pulmonary disease?
The use of electronic cigarettes, or “vaping,” has garnered significant popularity and attention in recent years. Its pulmonary and systemic effects have yet to be fully studied and quantified, and recent reports of vaping-related illnesses and deaths have brought the clinical consequences of vaping into the public spotlight. This report describes the case of a 34 year old woman who presented to clinic with new-onset cough and dyspnea, shortly after beginning to use electronic cigarettes. Imaging demonstrated new micronodular opacities and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, while pathology confirmed granulomatous disease. After she received counseling and successfully quit vaping, her symptoms resolved and repeat imaging demonstrated resolution of parenchymal findings and lymphadenopathy. This case report therefore presents a longitudinal narrative of reversible vaping-related pulmonary granulomatous disease.
Is vaping a pulmonary granulomatous disease?
This case of pulmonary granulomatous disease related to vaping describes unintended consequences from vaping. Vaping simulates the experience of traditional cigarette smoking by vaporizing liquids which are then inhaled. 1 Despite a relative lack of evidence-based literature, many consider vaping to be lower risk when compared to traditional cigarette smoking, presumably due to the absence of conventionally-visualized and combustion-produced toxicants, and their purported role in assisting with traditional smoking cessation. [1], [2], [3]
What are the causes of granulomatous disease?
Chronic granulomatous disease is caused by changes ( mutations) in one of five genes ( CYBA, CYBB, NCF1, NCF2, or NCF4 ). Each gene encodes a different part (subunit) of an enzyme called NADPH oxidase, which is essential to the immune system. One function of this enzyme is to help make toxic substances that are used to kill bacteria and fungi that invade the body before they can cause infection. It may also play a role in regulating the activity of immune cells that help manage the inflammatory response. Mutations in these genes lead to reduced levels of NADPH oxidase and in severe cases, no enzyme is produced. As a result, the immune system can not function properly, leaving the body vulnerable to frequent infections and chronic inflammation. [3]
When does granulomatous disease develop?
The features of the condition usually develop in infancy or early childhood; however, milder forms may be diagnosed in the teen years or even in adulthood.
How is chronic granulomatous disease inherited?
When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by changes ( mutations) in the CYBA, NCF1, NCF2, or NCF4 genes, it is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner . [5] [3] This means that a person must have a change in both copies of the disease-causing gene in each cell. The parents of an affected person usually each carry one mutated copy of the gene and are referred to as carriers. Carriers typically do not show signs or symptoms of the condition. When two carriers of an autosomal recessive condition have children, each child has a 25% (1 in 4) risk to have the condition, a 50% (1 in 2) risk to be a carrier like each of the parents, and a 25% chance to not have the condition and not be a carrier.
What blood test is used to diagnose granulomatous disease?
Specialized blood tests, such as the nitroblue tetrazolium test and/or flow cytometry with dihydrorhodamine, can then be ordered to confirm the diagnosis. Both of these tests can be used to determine whether or not the immune cells are making toxic substances that the body uses to fight infections. [1] [2]
How much risk of autosomal recessive disease?
When two carriers of an autosomal recessive condition have children, each child has a 25% (1 in 4) risk to have the condition, a 50% (1 in 2) risk to be a carrier like each of the parents, and a 25% chance to not have the condition and not be a carrier. When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by mutations in the CYBB gene, ...
Which genes are related to autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease?
CYBA, NCF1, NCF2, and NCF4 (the genes related to autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease)
Is a bone marrow transplant considered a granulomatous transplant?
A bone marrow transplant ( allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or HSCT) may be used to treat and possibly cure chronic granulomatous disease , however HSCT has serious risks including the possibility of severe disability or death. Although the risks associated with HSCT are decreasing due to medical advances, HSCT is usually only considered for those severely affected by chronic granulomatous disease. [1] [2] [4] [5]
Where does granulomatous disease develop?
People with chronic granulomatous disease may develop infections in their lungs, skin, lymph nodes, liver, stomach and intestines, or other areas. They may also develop clusters of white blood cells in infected areas. Most people are diagnosed with CGD during childhood, but some people may not be diagnosed until adulthood.
What is a granulomatous?
Chronic granulomatous (gran-u-LOM-uh-tus) disease (CGD) is an inherited disorder that occurs when a type of white blood cell (phagocyte) that usually helps your body fight infections doesn't work properly. As a result, the phagocytes can't protect your body from bacterial and fungal infections.
How does CGD affect the immune system?
People with CGD inherit the gene mutation from a parent. The genes normally produce proteins that form an enzyme that helps your immune system work properly. The enzyme is active in white blood cells (phagocytes) that catch and destroy fungi and bacteria to protect you from infections.
Which is more likely to have CGD?
Boys are more likely to have CGD.
What are the symptoms of CGD?
Signs and symptoms associated with infections include: Fever. Chest pain when inhaling or exhaling. Swollen and sore lymph glands. A persistent runny nose.
What is a granulomatous disease?
Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a genetic disorder in which white blood cells called phagocytes are unable to kill certain types of bacteria and fungi. People with CGD are highly susceptible to frequent and sometimes life-threatening bacterial and fungal infections.
What causes CGD?
CGD is caused by defects in an enzyme, NADPH oxidase, that phagocytes need to kill certain bacteria and fungi. Mutations in one of five different genes can cause these defects.
What is CGD in medical terms?
CGD is a primary immune deficiency disease (PIDD). For more information on PIDD research and patient care at NIAID, visit the NIAID PIDD site.
What is the best treatment for CGD?
People with CGD take lifelong regimens of antibiotics and antifungals to prevent infections. Injections with interferon gamma, a protein that improves the activity of phagocytes, also may help reduce the number of severe infections. Abscesses need aggressive care that may include surgery. Granulomas may require steroid therapy.
Can granulomas cause autoimmune disease?
In addition, heart or kidney problems, diabetes, and autoimmune disease may occur in people with CGD, but this varies depending on which gene is mutated.
Can people with CGD participate in clinical research?
People with CGD can participate in NIAID-supported clinical research. CGD is a primary immune deficiency disease (PIDD). For more information on PIDD research and patient care at NIAID, visit the NIAID PIDD site.
What diseases are caused by smoking e-cigarettes?
By 2016, investigators found people who used e-cigarettes were 30 percent more likely to have developed a chronic lung disease, including asthma, bronchitis and emphysema, than nonusers.
What are the carrier oils in vaping?
Carrier oils, such as vitamin E acetate, heavy metals, flavorings and other toxins have all been implicated. The vast majority of cases have involved vaping marijuana's psychoactive ingredient, THC. And in many cases, counterfeit vapes were used.
How does electronic cigarettes affect the lung?
The first study on the long-term health effects of electronic cigarettes finds that the devices are linked to an increased risk of chronic lung diseases , according to research published Monday in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. The study included 32,000 adults in the U.S.
Do e-cigarettes cause lung problems?
Those who smoked regular, combustible cigarettes had a higher risk of developing chronic lung diseases than those who used only e-cigarettes. But the study also found many adult smokers who tried e-cigarettes ended up using both forms of tobacco.
Does vaping cause physical damage?
The research adds to a growing body of evidence that vaping can cause physical harm, whether it's chemical burns to lung tissue, toxic metals that leave lasting scars on lungs, vitamin E oil that clogs lungs or even overheated batteries that explode.
Does vaping harm your lungs?
Vaping can harm your lungs relatively quickly, increasing the risk of conditions like asthma and bronchitis. New research explores the long-term health effects of using e-cigarettes. Hollie Adams / Bloomberg via Getty Images file.
What are the risks of vaping?
Other key points about vaping use include: 1 You can vape drugs other than nicotine, such as THC and CBD 2 It is possible to overdose on nicotine through vaping 3 Addiction to nicotine is also a serious side effect of vaping
Why is vaping addictive?
Vaping nicotine is addictive because of the way it works in your brain. Nicotine enters the brain quickly to activate reward pathways and cause the release of endorphins, your body’s natural pain-killers. Vaping is a particularly powerful way of exposing your brain to nicotine because the juices used have such a concentrated amount of nicotine.
How do you know if you're vaping too much?
How can you tell if someone is vaping too much? One study has shown that glycol and glycerin, two ingredients commonly used in vape juices, are upper airway irritants that can cause irritation of the throat and mouth as well as trigger a dry cough. But perhaps the biggest symptom of vaping too much is developing an addiction to nicotine, the chemical most commonly vaped.
Why is vaping good for you?
Vaping is a particularly powerful way of exposing your brain to nicotine because the juices used have such a concentrated amount of nicotine. The liquid nicotine used in e-cigarettes is absorbed far more quickly compared to nicotine from tobacco in regular cigarettes.
Does a vaporizer have nicotine?
Cannabidiol (CBD) vaporizers don’t contain nicotine or THC, but they can still cause side effects. There is minimal research on the side effects of vaping CBD, but some general side effects of vaping CBD that have been reported include:
Can you vape with THC?
Stomach: Vomiting and nausea. Other key points about vaping use include: You can vape drugs other than nicotine, such as THC and CBD.
Does vaping cause hallucinations?
They found that vaping was associated with increased effects of the drug, increased incidence of adverse effects (just as anxiety and paranoia) and impairments in both cognition and motor abilities. One person in the study hallucinated after vaping marijuana oil.
What is a vape pen?
With vaping, a device (typically a vape pen or a mod — an enhanced vape pen — that may look like a flash drive) heats up a liquid ( called vape juice or e -liquid) until it turns into a vapor that you inhale. “Vaping is a delivery system similar to a nebulizer, which people with asthma or other lung conditions may be familiar with,” says Broderick. ...
What is the chemical that can damage your lungs?
Acrolein: Most often used as a weed killer, this chemical can also damage lungs.
What is the condition called when you get sick from eating popcorn?
“Popcorn lung” is another name for bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), a rare condition that results from damage of the lungs’ small airways. BO was originally discovered when popcorn factory workers started getting sick. The culprit was diacetyl, a food additive used to simulate butter flavor in microwave popcorn.
Is second hand vapor safe?
Secondhand Vapor Isn’t Safe Either. It’s a myth that secondhand emissions from e-cigarettes are harmless. Many people think the secondhand vapor is just water, but this couldn’t be farther from the truth. The vapor emitted when someone exhales contains a variety of dangerous substances, which may include: Nicotine.
Does vaping affect the lungs?
Instead of bathing lung tissue with a therapeutic mist, just as a nebulizer does, vaping coats lungs with potentially harmful chemicals. E-liquid concoctions usually include some mix of flavorings, aromatic additives and nicotine or THC (the chemical in marijuana that causes psychological effects), dissolved in an oily liquid base.
What was the diagnosis of a 34 year old woman who had a dry cough and dyspnea?
A 34 year old woman presented to clinic with dry cough and dyspnea. She was a former cigarette smoker (four pack-years, quit at age 32). Her medical history was significant for a low-grade carcinoid tumor, which was discovered the year prior when she had sought evaluation for recurrent pneumonia and wheezing. At that time, due to airway obstruction, she had undergone right middle and lower lobectomies, and her symptoms resolved shortly thereafter.
Is vaping a pulmonary disease?
The use of electronic cigarettes, or “vaping,” has garnered significant popularity and attention in recent years. Its pulmonary and systemic effects have yet to be fully studied and quantified, and recent reports of vaping-related illnesses and deaths have brought the clinical consequences of vaping into the public spotlight. This report describes the case of a 34 year old woman who presented to clinic with new-onset cough and dyspnea, shortly after beginning to use electronic cigarettes. Imaging demonstrated new micronodular opacities and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, while pathology confirmed granulomatous disease. After she received counseling and successfully quit vaping, her symptoms resolved and repeat imaging demonstrated resolution of parenchymal findings and lymphadenopathy. This case report therefore presents a longitudinal narrative of reversible vaping-related pulmonary granulomatous disease.
Is vaping a pulmonary granulomatous disease?
This case of pulmonary granulomatous disease related to vaping describes unintended consequences from vaping. Vaping simulates the experience of traditional cigarette smoking by vaporizing liquids which are then inhaled. 1 Despite a relative lack of evidence-based literature, many consider vaping to be lower risk when compared to traditional cigarette smoking, presumably due to the absence of conventionally-visualized and combustion-produced toxicants, and their purported role in assisting with traditional smoking cessation. [1], [2], [3]
