The evidence against vaping is mounting, and a new study now links e-cigarettes with an increased risk for broken bones. Over time, vaping appears to increase the risk for fracture of the hip, spine and wrist by 46%, according to the findings.
What are the physiological effects of smoking e-cigarettes?
What is the strongest link to e-cigarettes?
Can vaping affect spinal fusion?
When were electronic cigarettes invented?
Does vaping cause inflammation?
Is e-cigarette smoke a carcinogen?
Is e-cigarettes healthier than conventional cigarettes?
See 2 more
About this website

Does vaping reduce bones?
The study also found that: A greater percentage of nonsmokers felt that cigarettes “definitely” impaired fracture healing (29.4% of nonsmokers versus 20% of smokers). Concerning cigarette alternatives (e-cigarettes and vapes), 22.8% of nonsmokers and 14.7% of smokers said they “definitely” impaired fracture healing.
Can nicotine weaken your bones?
Smoking affects the body's ability to absorb calcium, leading to lower bone density and weaker bones. Nicotine slows the production of the bone-forming cells that are so crucial to healing.
What damage does vape do to your body?
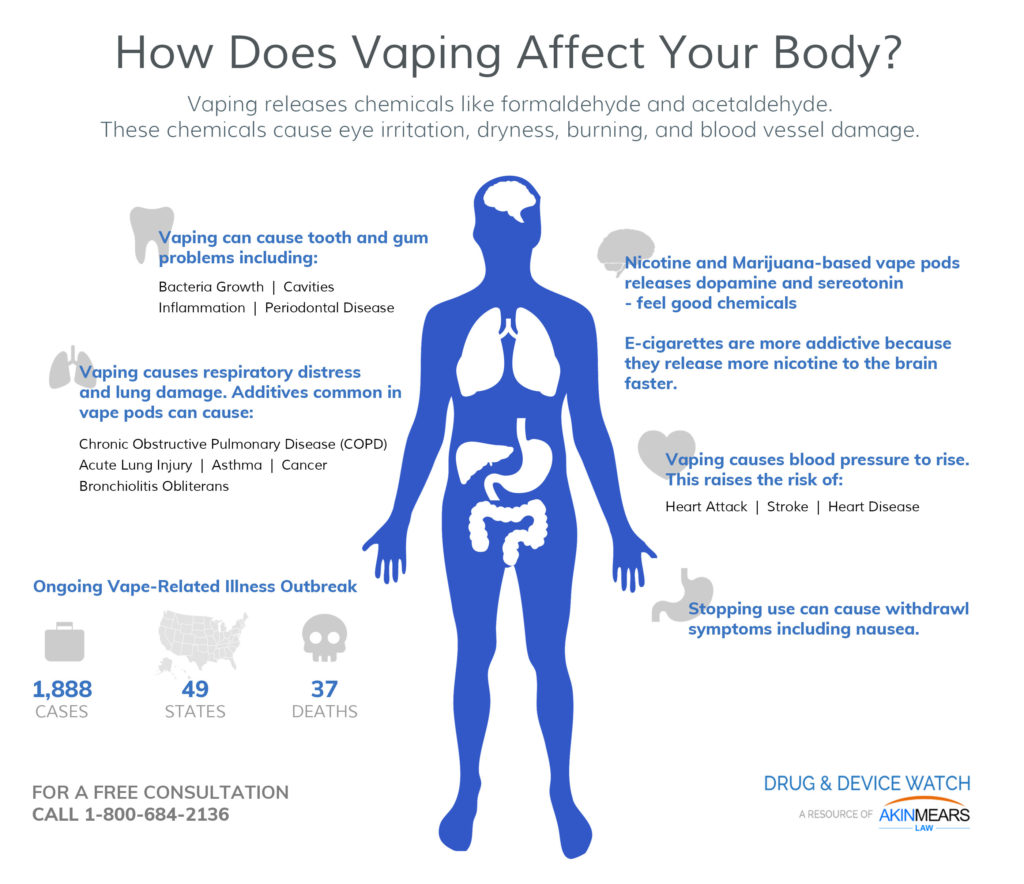
2: Research suggests vaping is bad for your heart and lungs. It causes you to crave a smoke and suffer withdrawal symptoms if you ignore the craving. Nicotine is a toxic substance. It raises your blood pressure and spikes your adrenaline, which increases your heart rate and the likelihood of having a heart attack.
Does vaping affect calcium?
Our experiment showed that electronic cigarette vapor did not have a statistically significant effect on the mice#s blood calcium levels. However, there was an increase in their calcium levels by the end of the week of testing, which was not shown by the control group (whose blood calcium levels fluctuated).
Can vaping cause osteoporosis?
E-cigarette carcinogens have shown to have a toxic effect on osteoblast cells, and long-term use may decrease bone mineral density and increase the future risk for osteoporosis.
How do you increase your bone density?
Include plenty of calcium in your diet. Good sources of calcium include dairy products, almonds, broccoli, kale, canned salmon with bones, sardines and soy products, such as tofu. If you find it difficult to get enough calcium from your diet, ask your doctor about supplements.
What are the symptoms of vaping too much?
Symptoms include:Persistent cough.Chest pain.Shortness of breath.Some users may even experience diarrhea, vomiting, nausea and fatigue before any breathing problems develop.
What are 5 dangers of vaping?
Vaping has been linked to lung injury.Rapid onset of coughing.Breathing difficulties.Weight loss.Nausea and vomiting.Diarrhea.
How much vaping is too much?
Even today, many high-profile sources list the toxic dose of nicotine (the LD50 – or the dose that will kill about half of people exposed) as between 30 and 60 mg. To put this in context of vaping, this would be about 4 ml of 12 mg/ml e-liquid. d.
What does nicotine do to your bones?
The nicotine in cigarettes slows the production of bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) so that they make less bone. Smoking decreases the absorption of calcium from the diet. Calcium is necessary for bone mineralization, and with less bone mineral, smokers develop fragile bones (osteoporosis).
How much nicotine affects bone healing?
Simply stated, smokers take longer to heal from fractures. In recent research, smokers who broke their leg took 62% more time to heal than non-smokers.
Does nicotine affect vitamin D?
Cigarette smoke decreases the production of the active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) in lung epithelial cells (20), which may be overcome with higher serum levels of the substrate (25-hydroxyvitamin D). Additionally, cigarette smoke may affect expression levels of the vitamin D receptor (21).
How does nicotine affect bone growth?
Smoking reduces the blood supply to the bones and to many other body tissues. The nicotine in cigarettes slows production of bone-producing cells, called osteoblasts. Smoking decreases the body's absorption of calcium, which is necessary for vital cellular functions and bone health.
Does nicotine make you heal slower?
Nicotine effects on your body: Nicotine narrows the small blood vessels that normally bring oxygen, nutrients, and healing factors to your injured area. This slows down healing and may extend the duration of your pain. Nicotine causes the platelets (important components in your blood) to clump and form clots.
Does nicotine affect your muscles?
It weakens your body's collagen: Nicotine is toxic for the body. One effect of this toxicity is that it breaks down the collagen in the skin and body's connective tissues (including muscles, bones, blood vessels, the digestive system, and tendons) faster than what would occur naturally over time.
Why does nicotine slow down healing?
“Basically, nicotine makes your blood vessels smaller and your blood stickier,” Spiegel says. As a result, blood circulation is reduced, especially to small microvessels found in the skin, making it much harder for the body to repair injuries.
What are the physiological effects of smoking e-cigarettes?
Primary research suggests that the principle mechanism behind physiological consequences related to e-cigarette exposure is oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress and inflammation are intricately linked bidirectional processes that together lead to cellular and tissue damage [13]. E-cigarette vapor itself, like cigarette smoke, is a potent source of ROS [14]. When using an e-cigarette, ROS are directly inhaled into the lungs and play an integral role in stimulating inflammatory signaling cascades [14,15]. Moreover, inflammation stemming from exposure to toxic chemicals in e-cigarette vapor results in the recruitment of immune cells like macrophages and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Subsequently, inflammatory proteins and immune cells generate ROS that work in a feed-forward manner to increase inflammation and cellular damage, which can have widespread effects on various organ systems.
What is the strongest link to e-cigarettes?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), vitamin E acetate , a common additive in e-cigarette devices, represents the strongest link to e-cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) outbreak [5].
Can vaping affect spinal fusion?
The outcome and results of spinal fusion operations in patients who admit to e-cigarettes use are poorly described in the literature. A 2019 review by Amaro et al. provided a review of available knowledge on the effects of vaping on orthopedic surgeries that are pertinent to spinal fusions [30]. While the effects of e-cigarettes use on spinal fusion is not well documented, experiments of posterolateral spinal fusions in the rabbit model demonstrate that nicotine alone can affect surgical outcomes [30]. A 1995 study by Silcox et al. demonstrated systemic nicotine significantly increased pseudoarthrosis rate to 100% compared to 44% in control animals in a rabbit model of posterolateral spine fusion [31]. A 2000 study by Theiss et al. revealed nicotine alone inhibits the expression of multiple cytokines with a variety of functions during spine fusion [32].
When were electronic cigarettes invented?
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) were first designed by a Chinese pharmacist in 2003 [1] . In 2006, e-cigarettes were introduced to the United States market as a smoking cessation tool marketed as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes [2]. According to a recent study of U.S. adults, 95% of those interviewed believed e-cigarettes to be “cleaner and healthier” than conventional products, suggesting the validity of introductory claims were widely accepted by the general public [3]. The result was exponential growth in popularity among traditional combustible cigarette smokers, who represent 64.7% of e-cigarette users [4] . In a survey of approximately 15,000 U.S. adults between 2010 and 2013, e-cigarette use increased from 1.8% to 13%, approximately a seven-fold increase [4]. Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) evolved from traditional disposable e-cigarettes, which are similar to conventional cigarettes in flavor and appearance, to large-size tank devices, and finally “pod-mod” devices such as JUUL® [2]. The JUUL® was introduced in 2015, and immediately gained popularity amongst the youth due to its sleek design, desirable flavors, and the ability to smoke discreetly in prohibited locations [2]. The usage of ENDS has increased in young adults from 1.5% in 2011 to 20.8% in 2018 [2].
Does vaping cause inflammation?
Recent data by Crotty Alexander et al. suggests that e-cigarette exposure triggers an inflammatory response that results in cellular damage to the airways, specifically by disrupting pulmonary epithelial barrier function [10]. In a feed-forward manner , disruption of barrier function and continued exposure to chemical toxins found in e-cigarette vapor contributes to systemic inflammation that can result in downstream organ pathologies such as renal fibrosis [10]. An essential component of inflammation is oxidative stress. Oxidative stress, which is generated by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), can activate the transcription of inflammatory genes such as IL-8, a potent chemokine that recruits leukocytes and is involved in chronic inflammation [11]. Several groups have clearly demonstrated the link between vaping and oxidative stress using both in vivo and in vitro laboratory models. Lerner et al. measured intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor for three days (five hours total exposure time) [11]. GSH is an essential endogenous antioxidant that maintains cellular redox balance by responding to ROS stress [11]. The authors found that there was a significant decrease in GSH levels in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor compared with air-exposed controls (P < 0.05) [11]. Additionally, there were modulations in the balance between the reduced and oxidized forms of GSH in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor [11]. Ganapathy et al. found that human epithelial bronchial cells exposed to e-cigarette vapor for two weeks in vitro had significantly increased levels of oxidative damage, indicated by 8-oxo-dG DNA lesions, compared to the control group of air-only (P < 0.05) [12]. Cells exposed to e-cigarette vapor showed significantly increased levels of oxidative damage compared to cells exposed only to cigarette smoke (P < 0.05) [12]. Moreover, the authors reported a significant decrease in total antioxidant capacity in cells exposed to either e-cig vapor or cigarette smoke (P < 0.05), with no significant difference between the two experimental groups [12].
Is e-cigarette smoke a carcinogen?
The general consensus is that e-cigarette vapor has substantially lower levels of carcinogens and toxins found in traditional cigarette smoke. For example, Tayyarah et al. report that cigarette smoke contains between 3069 and 3350 μg/puff of the 55 harmful and potentially harmful constituents (HPHC) measured in the study [6]. Conversely, e-cigarette vapor contained <2 μg/puff of HPHCs, or ~99% less analytes than cigarettes [6]. However, there are novel toxicology risks associated with e-cigarettes that must be further evaluated. E-cigarettes have heating coils that are made of various metallic compounds and can be used with thousands of different e-liquids with various chemical flavoring additives [7]. Williams et al. quantified the abundance of metallic elements in various e-liquids using induced coupled plasma-optical emissions spectroscopy (ICP-OES) [8]. The authors reported that e-cigarette vapor contained aerosol particles >1µm of tin, silver, iron, nickel, aluminum, silicate [8]. Strikingly, nine of the 11 metals detected in e-cigarette vapor were equal to or greater than the concentration detected in cigarette smoke [8]. All of these metals are associated with human toxicity at high doses, particularly in the nervous, renal, and respiratory systems [8].
Is e-cigarettes healthier than conventional cigarettes?
According to a recent study of U.S. adults, 95% of those interviewed believed e-cigarettes to be “cleaner and healthier” than conventional products, suggesting the validity of introductory claims were widely accepted by the general public [3].
What is a vape cartridge?
Vape cartridges, like traditional cigarettes, contain nicotine. Combined with other chemicals and artificial flavors, the nicotine is heated and inhaled as a vapor. Like with regular cigarettes, the act of vaping releases dopamine into the system which produces a good feeling – that satisfaction as highlighted in cigarette marketing in the past.
Does nicotine make you feel pain?
Cleveland Clinic suggests that consumption of nicotine will worsen pain over time, particularly in places where blood has difficulty reaching. It is possible, too, to feel pain while quitting. It’s a sensation that can improve, however, by replacing smoking habits with healthier activities. At Bon Secours Virginia Orthopaedic & Spine Specialists, ...
Does vaping cause joint pain?
The Connection Between Vaping and Joint Pain. If you smoke, and want to quit, any day is a great to begin. Whether you have smoked regularly for a short time or for years, completing a full day without a cigarette offers healthful benefits to your body. You lower the risk for heart attack, and your oxygen levels significantly improve.
Does vaping cause blood to flow slower?
Initially, a person who vapes may feel a brief respite from discomfort, but over time vaping can lead to bigger problems. The more one smokes or vapes, the slower the flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
Is vaping safer than smoking?
(Source: Truth Initiative) While some view vaping as less harmful than smoking, it doesn’t necessarily mean vaping is risk-free, especially where joint pain is concerned.
Why does vaping hurt?
There could be various reasons for chest pain from vaping. Excessive heat, high nicotine, or maybe even the specific flavorings in a particular e-liquid could be the cause.
What are the side effects of vaping?
Coughing. Headaches. Dizziness or headrush. Weight loss/gain. Nausea. Tired and fatigued. Chest pain from vaping. Although vapes are not medical devices, side effects for the user may occur. But these side effects are not a given.
How to stop dizziness when vaping?
If you’re concerned about dizziness or the feeling of being lightheaded, the best course of action is to lower your nicotine or the amount you vape in short periods. If you’d prefer to not lower your consumption, it’s something that will likely go away as your body gets accustomed to nicotine.
What to do if you have chest pains when vaping?
Then maybe you can lower the power, reduce your nicotine, change your atom izer or coil , or change your flavor . Essentially, try and change your entire set up if you have to.
Does nicotine cause headaches?
Alkaloids have a physiological effect on the user, and cessation from habitual usage may cause headaches. Nicotine is the major alkaloid in tobacco, accounting for about 95% of the alkaloid content, but there are other tobacco minor alkaloids in tobacco smoke, not present in e-liquid.
Can vaping cause dizziness?
Dizziness or headrush. Similar to the feeling of smoking for the first time, it’s not uncommon to experience lightheadedness and dizziness from vaping. Also similar to smoking, this typically will stop presenting itself the more you consume.
Can you get a sore throat from vaping?
Some coils used in vaping are nickel-based, and it’s not uncommon for users to discover they have an allergy to nickel. Also, several reports online can be found associating a sore throat with high nicotine, especially when used with high levels of propylene glycol (50% or more).
What are the side effects of vaping fluid?
The following side effects may be experienced from excessive vaping with fluid that contains nicotine: Gum inflammation. Plaque accumulation. Dry mouth. Nicotine in vape liquids may also cause or more of the following side effects: Receding gums. Periodontitis.
How to minimize side effects of vaping?
How to Minimize Side Effects. If you have to vape, remember that you should responsible enough to take care of your teeth. Consider the following to help reduce the risk for side effects: Rehydrate after you vape. This will help prevent bad breath and dry mouth. Always drink water after you vape.
How to stop nicotine from affecting gums?
Reduce your nicotine intake. Choose juices without nicotine or at least those with very low nicotine content. This can help limit the negative effects of nicotine on your gums and teeth.
What are the ingredients in vaping?
What’s clear is that there are three ingredients in e-liquids that are known to have harmful effects to oral health. These are: Menthol. Propylene glycol. Nicotine. These ingredients may also cause vaping teeth stain. Flavored e-juice is also known to cause more gum inflammation than the non-flavored kind.
What is the chemical in e-cigarettes?
Propylene glycol, glycerin, an array of flavors largely make up the ingredients. The electric component of e-cigarettes and vaping devices converts the liquid into an aerosol. The e-liquid is prepared in a preloaded cartridge for insertion into the device; it may also be mixed specifically at a store or using a DIY kit.
What happens if you eat e-cig?
E-cig aerosols can cause inflammation and DNA damage on the mouth. This will cause the cells to lose their ability to reproduce and thrive, speeding up cell aging and eventually causing death. This can lead to various oral health problems including:
Does vaping cause cell death?
Bone loss. Periodontal diseases. Researchers are constantly trying to understand how vaping can actually lead to cell death and more long-term research is required. For now, people need to become more aware of the health risks of using these gadgets.
What are the physiological effects of smoking e-cigarettes?
Primary research suggests that the principle mechanism behind physiological consequences related to e-cigarette exposure is oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress and inflammation are intricately linked bidirectional processes that together lead to cellular and tissue damage [13]. E-cigarette vapor itself, like cigarette smoke, is a potent source of ROS [14]. When using an e-cigarette, ROS are directly inhaled into the lungs and play an integral role in stimulating inflammatory signaling cascades [14,15]. Moreover, inflammation stemming from exposure to toxic chemicals in e-cigarette vapor results in the recruitment of immune cells like macrophages and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Subsequently, inflammatory proteins and immune cells generate ROS that work in a feed-forward manner to increase inflammation and cellular damage, which can have widespread effects on various organ systems.
What is the strongest link to e-cigarettes?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), vitamin E acetate , a common additive in e-cigarette devices, represents the strongest link to e-cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) outbreak [5].
Can vaping affect spinal fusion?
The outcome and results of spinal fusion operations in patients who admit to e-cigarettes use are poorly described in the literature. A 2019 review by Amaro et al. provided a review of available knowledge on the effects of vaping on orthopedic surgeries that are pertinent to spinal fusions [30]. While the effects of e-cigarettes use on spinal fusion is not well documented, experiments of posterolateral spinal fusions in the rabbit model demonstrate that nicotine alone can affect surgical outcomes [30]. A 1995 study by Silcox et al. demonstrated systemic nicotine significantly increased pseudoarthrosis rate to 100% compared to 44% in control animals in a rabbit model of posterolateral spine fusion [31]. A 2000 study by Theiss et al. revealed nicotine alone inhibits the expression of multiple cytokines with a variety of functions during spine fusion [32].
When were electronic cigarettes invented?
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) were first designed by a Chinese pharmacist in 2003 [1] . In 2006, e-cigarettes were introduced to the United States market as a smoking cessation tool marketed as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes [2]. According to a recent study of U.S. adults, 95% of those interviewed believed e-cigarettes to be “cleaner and healthier” than conventional products, suggesting the validity of introductory claims were widely accepted by the general public [3]. The result was exponential growth in popularity among traditional combustible cigarette smokers, who represent 64.7% of e-cigarette users [4] . In a survey of approximately 15,000 U.S. adults between 2010 and 2013, e-cigarette use increased from 1.8% to 13%, approximately a seven-fold increase [4]. Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) evolved from traditional disposable e-cigarettes, which are similar to conventional cigarettes in flavor and appearance, to large-size tank devices, and finally “pod-mod” devices such as JUUL® [2]. The JUUL® was introduced in 2015, and immediately gained popularity amongst the youth due to its sleek design, desirable flavors, and the ability to smoke discreetly in prohibited locations [2]. The usage of ENDS has increased in young adults from 1.5% in 2011 to 20.8% in 2018 [2].
Does vaping cause inflammation?
Recent data by Crotty Alexander et al. suggests that e-cigarette exposure triggers an inflammatory response that results in cellular damage to the airways, specifically by disrupting pulmonary epithelial barrier function [10]. In a feed-forward manner , disruption of barrier function and continued exposure to chemical toxins found in e-cigarette vapor contributes to systemic inflammation that can result in downstream organ pathologies such as renal fibrosis [10]. An essential component of inflammation is oxidative stress. Oxidative stress, which is generated by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), can activate the transcription of inflammatory genes such as IL-8, a potent chemokine that recruits leukocytes and is involved in chronic inflammation [11]. Several groups have clearly demonstrated the link between vaping and oxidative stress using both in vivo and in vitro laboratory models. Lerner et al. measured intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor for three days (five hours total exposure time) [11]. GSH is an essential endogenous antioxidant that maintains cellular redox balance by responding to ROS stress [11]. The authors found that there was a significant decrease in GSH levels in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor compared with air-exposed controls (P < 0.05) [11]. Additionally, there were modulations in the balance between the reduced and oxidized forms of GSH in mice exposed to e-cigarette vapor [11]. Ganapathy et al. found that human epithelial bronchial cells exposed to e-cigarette vapor for two weeks in vitro had significantly increased levels of oxidative damage, indicated by 8-oxo-dG DNA lesions, compared to the control group of air-only (P < 0.05) [12]. Cells exposed to e-cigarette vapor showed significantly increased levels of oxidative damage compared to cells exposed only to cigarette smoke (P < 0.05) [12]. Moreover, the authors reported a significant decrease in total antioxidant capacity in cells exposed to either e-cig vapor or cigarette smoke (P < 0.05), with no significant difference between the two experimental groups [12].
Is e-cigarette smoke a carcinogen?
The general consensus is that e-cigarette vapor has substantially lower levels of carcinogens and toxins found in traditional cigarette smoke. For example, Tayyarah et al. report that cigarette smoke contains between 3069 and 3350 μg/puff of the 55 harmful and potentially harmful constituents (HPHC) measured in the study [6]. Conversely, e-cigarette vapor contained <2 μg/puff of HPHCs, or ~99% less analytes than cigarettes [6]. However, there are novel toxicology risks associated with e-cigarettes that must be further evaluated. E-cigarettes have heating coils that are made of various metallic compounds and can be used with thousands of different e-liquids with various chemical flavoring additives [7]. Williams et al. quantified the abundance of metallic elements in various e-liquids using induced coupled plasma-optical emissions spectroscopy (ICP-OES) [8]. The authors reported that e-cigarette vapor contained aerosol particles >1µm of tin, silver, iron, nickel, aluminum, silicate [8]. Strikingly, nine of the 11 metals detected in e-cigarette vapor were equal to or greater than the concentration detected in cigarette smoke [8]. All of these metals are associated with human toxicity at high doses, particularly in the nervous, renal, and respiratory systems [8].
Is e-cigarettes healthier than conventional cigarettes?
According to a recent study of U.S. adults, 95% of those interviewed believed e-cigarettes to be “cleaner and healthier” than conventional products, suggesting the validity of introductory claims were widely accepted by the general public [3].